Before choosing the best air-operated double-diaphragm (AODD) pump materials for your application, these fluid characteristics must be considered: temperature, abrasiveness, viscosity and overall chemical compatibility.
Selecting the right materials for an AODD pump is an essential step in achieving maximum performance and safety. Understanding the diaphragm pump material selection process will help decrease downtime while increasing reliability, performance and profitability.
Click the links below to learn more about each characteristic to consider when choosing pump material:
Chemical Compatibility
Diaphragm pump material selection is critical to its cost and durability.
First, make sure that the fluid you're moving is chemically compatible with the pump materials. This includes elastomers, castings, and possibly hardware if there are plans to submerge the pump. To do this, consult your AODD pump manufacturer’s chemical compatibility guide.
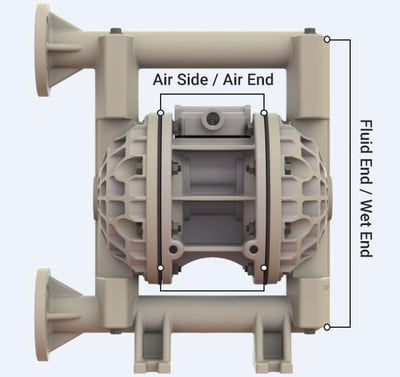
Fluid End/Wet End
The fluid and air sides of the pump are separated by the seal created with the diaphragms. It is critical to confirm the chemical compatibility for both the AODD pump’s wetted casting or pump body (chambers and manifolds) and the pump’s seals (diaphragms, valve balls and manifold seats/seat seals).
In many cases, there can be multiple materials that are chemically resistant. If this is the case, you want to understand the other fluid characteristics and how the pump will be used. For example, if you’re pumping an abrasive product, choose castings and elastomers that effectively handle abrasive products. If the fluid is flammable, choose a material that can be grounded, like a metal ATEX model. Sometimes it just comes down to cost. For example, PVDF (Kynar®) can handle most chemicals but is more costly than polypropylene. So if polypropylene is chemically compatible, you might select the lower-cost pump construction.
Air End/Non-Wet End
For the pump’s air side, select a chemically compatible material with the fluid being pumped.
The fluid being transferred doesn’t only contact the wetted side of the pump. The fluid is certain to encounter the air side of the unit, either via the environment around the pump or when a diaphragm fails. Many times, the surrounding environment can have chemical fumes, or the process in which the pump is installed can drip or splash chemicals during transfer. If that is the case, you need to make sure the air side (air valve, center block, air chambers, etc.) include chemically compatible materials of construction.
This is also true when a diaphragm failure occurs. When a diaphragm fails, the liquid can contact the pump’s air side. If not compatible, this can cause issues with the main air valve and pilot valve, as well as other systems tied into the same airline.
Using chemically compatible materials on both the air and wetted side will extend the life and performance of the pump and, in most cases, will be worth the additional upfront cost associated with some air side materials (such as stainless steel).
Fluid Attributes
Abrasive Fluids
If you’re pumping abrasive material, you may want to choose harder casting and seat materials. Both stainless steel and cast iron are great metal pump options for combating premature wear due to abrasives, while PVDF is best for plastic pumps in abrasive applications. If you’re questioning the effectiveness of a specific material, consult the AODD pump manufacturer for assistance.
Temperature Range (Fluid Being Pumped)
AODD pumps can handle a wide range of temperatures: cold fluids (consult factory when pumping fluids below freezing) and fluids up to 220 degrees Fahrenheit (104 degrees Celsius) and beyond. When exceeding 220 degrees Fahrenheit (104 degrees Celsius), consult the factory for guidance.
Fluid Viscosity
Viscosity of fluid being pumped is important to understand as it has a direct correlation to performance and material choice. For higher viscosity (thicker) products, heavy valve balls like stainless steel or PTFE might be needed in order to rise and fall in the thick fluid. This allows the pump to operate as intended. Lighter materials, like Santoprene, might not work as well with thick products as they have a tendency to float, affecting flow and pump performance.
Flammable Fluids
AODD pumps do not require electricity to run. Instead, they require compressed air. Due to the reciprocating movement of the diaphragm rod and potential for static build-up, AODD pumps with the proper provisions can be grounded for safe, reliable operation in explosive environments. This is critical when pumping flammable liquids or when a pump is in an environment where fumes are present.
Pump Material Physical Attributes
Pump Weight/Portable Applications
If an AODD pump is going to be used in a portable application, users might choose a lighter material if a cart or dolly is not an option. Specifically, in underground mining, AODD pumps are moved by hand, so weight is a big factor. Many customers will choose a lightweight plastic or aluminum unit over a heavier cast iron or stainless steel body. Some may use a smaller pump, like a 1 ½” or 2” unit instead of a 3”, which is considerably heavier.
Indoor or Outdoor Installation (UV Sunlight/Temperatures)
When purchasing a pump, you need to understand if the pump will be installed inside a facility or out in the elements. This is important for several reasons.
If the pump is to be installed in direct sunlight, you may choose a metallic unit over a plastic one. Over time, UV sunlight can break down plastic components, causing it to become brittle, potentially leading to issues.
Another factor is cold temperatures. If the pump experiences temperatures below freezing, make sure the fluid being moved is flushed. If the fluid freezes in the pump, it can damage castings and/or diaphragms. Alternately, heat trace is a common addition to piping and pumps that helps prevent freezing in harsh environments.
Surface Finish Requirements
Some applications, like food processing or personal care products, may require the surface finish to meet a specific smoothness. For example, 3-A certified units used to pump dairy products require a 32µ-in (Ra 0.8 µ-m) surface finish or better. On the other hand, an FDA-type application may require a less polished finish depending on how the pump is to be cleaned and sanitized.
Pump Elastomer Attributes
Each of the commonly offered diaphragm materials come with varying attributes. When applied correctly, these attributes can increase the MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure), ultimately reducing downtime. Below are some attributes about each elastomer or thermoplastic to consider when selecting them.
Rubber Materials (Diaphragms, Valve Balls, Seat/Seat Seals)
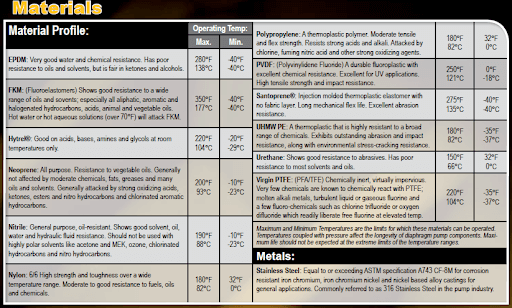
- Neoprene: Long-lasting elastomer but limited chemical resistance
- Nitrile (BN): Very popular with oils and hydrocarbons
- FKM Fluorocarbon (VT): Excellent chemical resistance with average flex-life
- EPDM (ND): Good chemical reliance and longevity
Thermoplastic Materials (Diaphragms, Valve Balls, Seat/Seat Seals)
- Santoprene (EPDM/Polypropylene cross-linked): Excellent chemical resistance, abrasion resistance and flex-life
- Hytrel (FDA): Used mainly for food processing applications for clean, hygienic services
PTFE (TF)
- PTFE: Best chemical resistance of any material but more costly
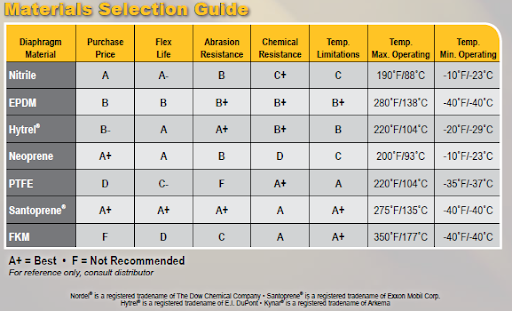
The material chart below offers you guidance when selecting the materials within your pump.
- Note all the chemically compatible materials.
- If the temperature is a factor, then choose the elastomers that work within that envelope.
- Are there abrasives present? If so, in most cases, that would exclude PTFE.
- If you have several diaphragm/seal material options, which one would be most economical? PTFE and Viton are the most expensive, while Santoprene and Neoprene are least costly.
- Which materials offer the longest flex-life? Santoprene and Neoprene offer the best flex-life, followed by Nitrile, EPDM and Hytrel. Viton and PTFE offer lower flex-life in general when chemical compatibility is not an issue.
Ultimately, it’s a balance between chemical resistance at a higher cost versus flex-life at a lower cost. In many applications, Santoprene is a very effective material because it offers much of the chemical resistance of PTFE, excellent flex-life and is very cost-effective. However, it has some chemical limitations, so check the chemical compatibility guide when making your choice.
Pump Wetted Casting Attributes
Each of the commonly offered diaphragm materials come with varying attributes. When applied correctly, these attributes can increase the MTBF, ultimately reducing downtime. Below are some attributes about each casting material to consider when selecting them.
Metal Casting Materials (Fluid Chambers, Manifolds, Seats, Diaphragm Plates)
- Aluminum: Strong and lighter weight compared to other metals, aluminum has average chemical resistance and is popular in paint, oil, gas and mining.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is very strong and abrasion resistant, but is heavy for mobile applications.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel has excellent chemical resistance and can be used for food processing applications because it’s easily cleaned and doesn’t corrode.
- Alloy C: While Alloy C is extremely chemically resistant for a metal product, it’s very costly.
Plastic Casting Materials (Fluid Chambers, Manifolds, Seats, Diaphragm Plates)
- Polypropylene: Polypropylene has strong chemical resistance for acids and caustics, is lightweight for mobile applications and can be very affordable depending on the pump size.
- PVDF: PVDF is more chemically resistant than polypropylene and can handle most acids and caustics, even at higher concentrations. PVDF is also a very strong plastic material and handles abrasion better than polypropylene.
- Conductive Acetal: Much like the chemical resistance of polypropylene, acetal can be used to prevent static discharge for pumping liquids that are flammable.
Customer Preference
Flexibility (Will the Pump Be Used for Multiple Chemicals/Applications?)
Some users find value in standardizing on one pump model to handle all needs of their plant. The initial investment may be greater upfront for an AODD pump that is PTFE-fitted, but might save you in the long run for the following reasons:
- Training for your staff on one specific pump model
- Standardization on repair parts and kits helps reduce inventory
- Common model helps keep mixed product batches consistent
- Cost savings as each model has been verified for chemical compatibility
Initial Cost/Purchase Price:
If initial cost is a driving factor in the decision-making process, when researching AODD pumps, evaluate all the materials that will work, then select the least-cost combination. Generally, aluminum casting pumps fitted with Nitrile elastomers is a reliable, low-cost option.
Certification Requirements (FDA/3-A, UL Listed, ATEX, CE, EHEDGE, ABS and Others)
If the pump needs to carry a specific certification, make sure it’s available in the material options that you are looking for. If a pump needs to be 3-A, for example, there will be a limited amount of available material options. Consult the AODD pump manufacturer for details.
Mixed Material Pumps
Some users find that mixing materials within the pump offers them the best overall performance. For example, some users will choose heavy PTFE valve balls in a Santoprene-fitted pump because the PTFE balls work well when pumping thicker viscosity products. Some may choose a hard valve seat like stainless steel in an aluminum pump to deal with abrasive materials. These models may not show in the standard price book but are available for purchase. Remember, you can always contact the AODD pump manufacturer for guidance.
Choosing the right materials for your AODD pump during the selection process can make all the difference in your safety and satisfaction. For additional information on selecting the AODD pump that is right for your application, please contact us today.
Find these tips useful? Share which tip helped you the most in the comments below.
.png?width=272&height=66&name=headLogo%20(1).png)





.png?width=300&height=71&name=Versamatic_white-logo%20(1).png)