 Air-operated double-diaphragm (AODD) pumps can handle a wide range of chemicals, flow rates and viscosities. They can also perform well in a variety of industries. The more you know about AODD pump specifications, the easier it will be to find the best pump for your application.
Air-operated double-diaphragm (AODD) pumps can handle a wide range of chemicals, flow rates and viscosities. They can also perform well in a variety of industries. The more you know about AODD pump specifications, the easier it will be to find the best pump for your application.
Before selecting a pump, you need to have a solid grasp of the application requirements and chemical media properties, as well as the AODD pump performance and size specifications necessary to perform the task.
Chemical Compatibility
The number one consideration when selecting a pump is chemical compatibility. This is for employee safety as well as prolonging the life of the pump. Because corrosion is a major concern with many chemicals, it’s important to select a pump manufactured from a material that is compatible with chemical media. To do this, consult your AODD pump manufacturer’s chemical compatibility guide or contact the factory for assistance.
Chemical resistance pertains to wetted components, elastomers and even center sections. Keep in mind when a diaphragm fails, the product will make its way into the center section of the pump.
The two main categories of pump materials to consider are metal and plastic.
- Metal: Durable and robust, perfect for abrasives and slurries. They include:
- Aluminum
- 316 Stainless Steel
- Cast Iron
- Alloy C
- Plastic: Sturdy but lightweight designs, providing a broad range of chemical compatibility. They include:
- Polypropylene
- Acetal
- Conductive Polypropylene
- Conductive Acetal
- Conductive PVDF
- PVDF/Kynar
- Nylon
The viscosity of fluid being pumped is also important to understand, as it has a direct correlation to AODD pump performance and material choice. For higher viscosity (thicker) products, heavy valve balls like stainless steel or PTFE might be needed in order to rise and fall in the thick fluid. This allows the pump to operate as intended. Lighter materials, like Santoprene, might not work as well with thick products as they have a tendency to float, affecting flow and pump performance.
Different diaphragm materials can handle a broad array of fluids and temperature ranges while others are better suited for abrasive media.
Pump Sizing and Performance Specifications
Sizing a pump for the operating parameters involves matching the flow and pressure rating of a pump with the flow rate and pressure required for the process. The desired flow rate in gallons per minute (gpm) or liters per minute (lpm) is an important factor to consider when specifying a pump.
Flow rate is the volume of fluid you can transport within a given time. Knowing the diaphragm pump flow rate will help you:
- Assess if an existing pump isn’t working efficiently
- Determine the correct pump for your application
AODD pumps can perform anywhere from 0 to 280 gpm (1,060 lpm). This is achieved with a simple adjustment of the air pressure or discharge head, giving AODD pumps an advantage over other pump technologies where it may be difficult or impossible to have that much control over the flow rate.
Desire a higher flow rate? You’ll need a larger pump with larger port sizes. The higher the flow rate, the faster your job gets done. This ensures deadlines are met and allows for increased production. In order to achieve maximum efficiency, it’s important to determine the flow rate.
How to Calculate the Flow Rate of an AODD Pump
To measure the flow of fluid within a pipe, you first need to understand how many strokes the pump is making per minute.
There are several apps that can track your count, or you can simply count how many happen in 10 seconds and then multiply that value by six. You will then reference the pump data sheet (AODD pump performance and specifications).
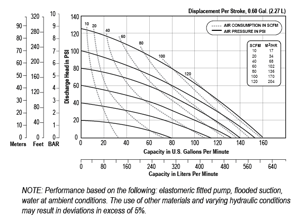
For example, let’s look at a 2” (51mm) Bolted Metal ATEX pump (ATEX-compliant pumps are suitable for use in explosive atmospheres when the equipment is properly grounded in accordance with local electrical codes).
For this pump, the displacement per stroke is 0.60 gal. (2.27 L). A stroke is one shift of the diaphragm assembly evacuating fluid out of one chamber.
A cycle is two strokes, or one on each side of the pump. To get the flow rate of your pump, multiply the number of strokes by the displacement per stroke.
Standard 1:1 ratio AODD pumps can produce pressures up to 125 psi (8.6 bar). With flow rates of up to 280 gpm (1,060 lpm), all without costly, sophisticated controls. Flow rates can be controlled to produce from zero to maximum flow simply by increasing or decreasing airflow and/or pressure.
Sizing an AODD Pump
To get the greatest efficiency and longevity when sizing an AODD pump, it is common to go up one porting size if possible.
For example, if you want to move 40 gpm (151 lpm) with 10 feet (3 meters) of head with a 1” (25mm) pump, most AODD manufacturers on the market could achieve that flow rate pumping water. Unfortunately, the pump would have to work at near its maximum capacity and stroke rate, thus leading to greater wear and reduced AODD pump efficiency.
By going up to the next pump size, you can run the pump significantly slower (at reduced strokes per minute), which will extend the life of the pump and enhance efficiencies (i.e., reduced air consumption).
Find the Right Pump for Your Project
Selecting the type of pump can be simplified if you know your:
- Application
- What type of fluid will you be pumping?
- Will the pump need to handle abrasive fluids, slurries or solids?
- Environment
- Will the pump be submerged or exposed to extreme temperatures?
- Is the fluid being pumped toxic or explosive?
- Sizing/porting requirements
- What is the desired flow rate?
- What is the port size and connection type you will be using?
The more you know about AODD pump specifications, the easier it will be to find the best pump for your application. No matter your industry, you can count on the consistency, reliability and trouble-free operation of Versamatic pumps.
If you have questions about AODD pump performance or specifications, feel free to contact us.
.png?width=272&height=66&name=headLogo%20(1).png)



.png?width=300&height=71&name=Versamatic_white-logo%20(1).png)